297 views
owned this note
# CS6332: List of useful tools for the class
## vim editor
Vim is a powerful text editor. The combination of multiple commands makes your life easier. I make a very introduction.
### Basic usage
Let's open a file with vim in terminal.
`vim <some file>`
There are some modes.
Normal mode: You can move.
- Move
- ↓: `j`
- ↑: `k`
- →: `l`
- ←: `h`
You can delete too.
- Delete
- character: `x`
- word: `dw` or `de`
- `dw`: until the next word
```txt
<cursor>word1␣word2␣word3
↓
<cursor>word2␣word3
```
- `de`: until the current word
```txt
<cursor>word1␣word2␣word3
↓
<cursor>␣word2␣word3
```
- line: `dd`
Edit mode: Do you want to write something? Type one of `o`, `O`, `i`, or `a`. Now, you can edit!
```txt
<O>
AB<i>C<cursor>D<a>E
<o>
```
You want to return back to the normal mode? Type `ESC`.
Are you fed up with this editor? In the normal mode, type `:x` or `:wq` to save (write) and quit. If you don't want to save, enter `:q!`.
### What's more
A good way to get started is to watch this video.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/13gNtgqzzmM?si=7FydcL0vcoxSbaAK" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" allowfullscreen></iframe>
- Or, type `vimtutor` on terminal.
- Or, visit online "vim-cheatsheet" sites.
- Or, read [MIT missing semester](https://missing.csail.mit.edu/2020/editors/)
## tmux
### Basic usage
`tmux` starts a new tmux sessions
A session has windows, and a window has panes.
- Session
- Detach: `C-b d`
- Re-enter the last detached session: `tmux a` (from terminal)
- Window
- create a new window: `C-b c` (`C-b` means type `control` key and `b` simultaneously)
- move to the window 0: `C-b 0`
- move to the window <num>: `C-b <num>`
- delete a window: `C-b &`
- Pane
- create a new pane vertically: `C-b %`
- create a new pane horizontally: `C-b "`
- delete: `C-b x`
- move to a next pane: `C-b o`
Hey! How can I scroll up and down? Use `C-b [` (copy-mode).
Video versions:
<iframe src="https://capture.dropbox.com/embed/rBeyb4bMtRRFnRnx?source=copy-embed" width="560" height="315" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
<iframe src="https://capture.dropbox.com/embed/mR5ERlKzVDUDIgH5?source=copy-embed" width="560" height="315" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
<iframe src="https://capture.dropbox.com/embed/pfV3Bg8owevRH9Zf?source=copy-embed" width="560" height="315" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
### How to customize
Edit `~/.tmux.conf`.
I recommend adding these lines at least.
```conf
set -g default-terminal "screen-256color" # colorful tmux
setw -g mode-keys vi # use vim in copy mode
```
### What's more
- [Cheatsheet](https://tmuxcheatsheet.com/)
- [MIT missing semester](https://missing.csail.mit.edu/2020/command-line/)
## pwntools
pwntools is a Python CTF framework. When you analyze a binary code in this course, this tool will be your friend.
### Basic usage
```python=
from pwn import *
context.clear(arch="amd64") # set cpu architecture
context.terminal = ["tmux", "splitw", "-h"] # set how it opens a tmux session
```
This imports a lot of functionality into the global namespace. You can now assemble, disassemble, pack, unpack, and many other things with a single function. [^pwn-intro]
[^pwn-intro]: https://docs.pwntools.com/en/stable/intro.html
The workflow to exploit a program with I/O will be like this.
```python=
# You will be given a binary, `bin_file`
p = process(bin_file) # spawn bin_file process
print(p.sendline(b"some random words to exploit the program"))
# p.send(b"string"): p.sendline(b"string") without a newline
print(p.recvline()) # output the process stdout
# p.recv(numb=4096, timeout=default): receive up to `numb` characters
```
Do you want to debug it? Sure. You can use `gdb` with pwntools.
```python=
p = process(bin_file) # start a process
# You can write gdb script with an optional argument. Start gdb process and let it monitor `p` process!
gdb.attach(p, gdbscript="""
break main
""")
p.sendline(b"hello") # you can send a line as before
p.recvline() # you can receive a line as before
p.interactive() # you can dive into gdb from here
```
- Write `.py` file
- Run it on `tmux`
- Debug it!
Demo:
<iframe src="https://capture.dropbox.com/embed/afo3aUnZlxpBLHAa?source=copy-embed" width="560" height="315" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
### What's more
[official documents](https://docs.pwntools.com/en/stable/)
## Regex
Regular expression. We use it to extract some patterns. You often need to get a specific type of input or output in binary.
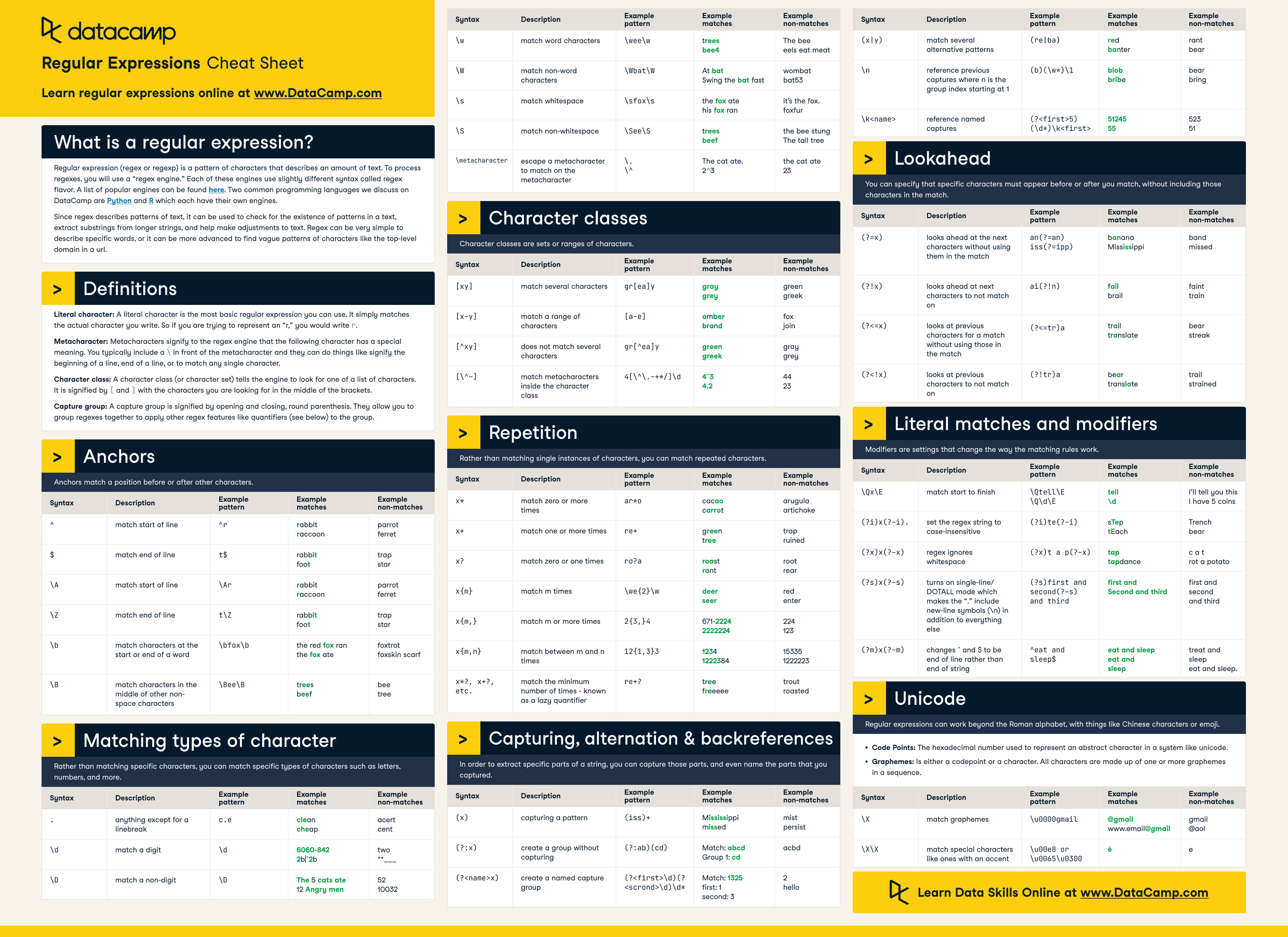
[pdf version](https://images.datacamp.com/image/upload/v1665049611/Marketing/Blog/Regular_Expressions_Cheat_Sheet.pdf)
### What's more
You can see if your pattern matches a string in the site below.
<https://regex101.com/>
###### tags: `cs6332`,`candl`,`course`